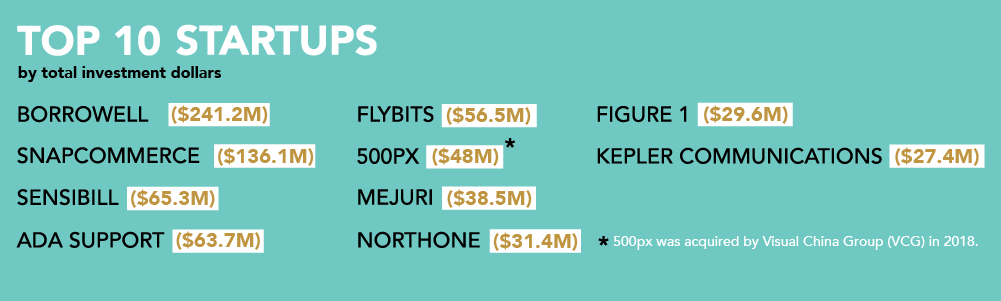
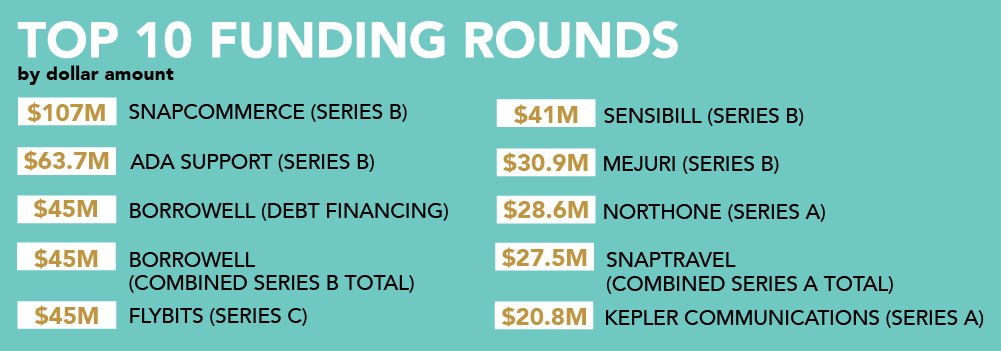
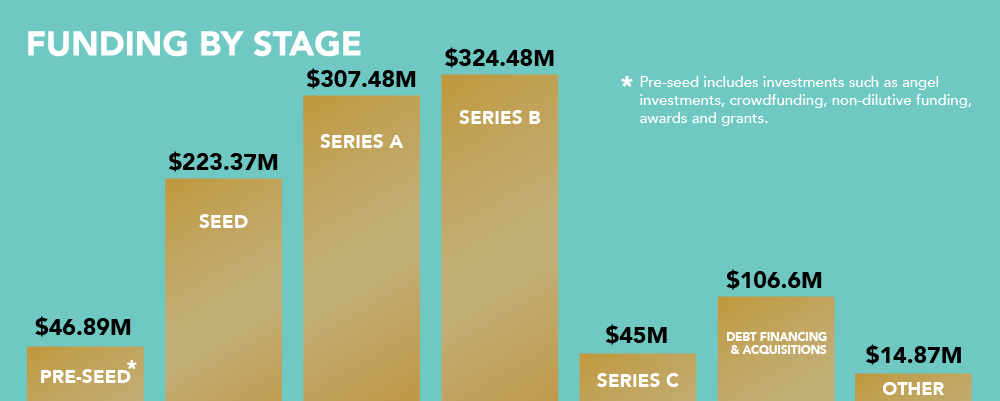
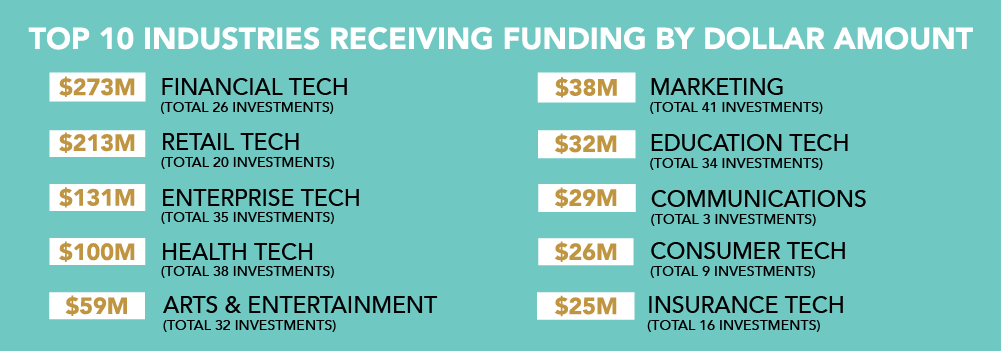
Fundraising is a thrilling time for any entrepreneur, especially early-stage founders. But with it comes numerous questions and challenges – most commonly, does my startup need a valuation before I can collect investment?
A SAFE (Simple Agreement for Future Equity) is a founder-friendly financing contract for startups in early financing rounds as an alternative to a convertible note. Rather than pricing the round, companies give investors the right to receive shares at a valuation set by future equity financing.
While equity financings trigger the SAFE to convert into equity, other triggers, such as a liquidity event or dissolution, allow investors to receive their money back in cash. This flexibility makes SAFEs a beneficial funding strategy for early-stage founders like you, who are still determining how to value their company.
Before we dive into specifics and must-know items about SAFEs, it is important to note that SAFEs are not the only vehicle used for pre-seed fundraising. Despite SAFEs being, as the name suggests (simple), not all investors use SAFEs as investment vehicles. SAFEs are still a relatively new legal invention with fewer guarantees which may result in some apprehension in the investor community. Utilized well, SAFEs can be an alternative to the Convertible Note that is more beneficial for founders and easier to understand. This article intends to teach you how and how not to use SAFE.
Why are SAFEs an important equity fundraising option for founders?
SAFEs simplify early-stage financing by
- Enabling you to raise capital when your company’s value is not certain.
- Using a standardized form that does not require significant modification.
- Minimizing the need for expensive and extensive negotiations.
SAFEs are a form of equity financing: As a founder, it is important to consider how much of your company you may give up with each SAFE you enter into. This is because the rate at which a SAFE converts to equity depends on several unknown factors. For example, if a SAFE converts to shares at a low valuation/share price, then the SAFE holders may end up with more shares in the company than the founder may have anticipated. As such, you must be aware of how future equity rounds will impact your cap table.
The number of shares a SAFE holder receives on conversion depends largely on the structure of the SAFE. A SAFE can have a valuation cap, a discount rate, both or neither. If both a discount and cap are present, a SAFE will convert under the option that provides the biggest discount, not both.
How to negotiate a valuation cap
While a SAFE is mostly standardized, one of the few negotiable terms is the valuation cap. Setting a post-money valuation cap determines the minimum level of ownership that a holder will receive at a priced round of financing. You can calculate ownership using the following formula:
As a founder, you may strive for higher valuation caps to retain more equity. However, investors may negotiate a lower valuation cap to ensure they receive a bonus for investing early. You should strive to find a balance to keep investors incentivized while ensuring you don’t dilute your ownership more than intended.
How to negotiate a discount rate
The discount rate is another common negotiable feature of a SAFE. It gives investors a direct discount on the price per share the SAFE will convert at relative to the price that the priced round investors will receive.
The discount rate for a SAFE is generally between 75-90% (reflecting a 10-25% discount). As a founder, you will want to negotiate a lower discount to retain more ownership. If you need urgent financing, the discount may be higher as the investor will have more bargaining power. However, keep in mind that an excessively high discount on SAFEs (30%+) can dissuade potential investors from investing in future rounds because the SAFE holders may be overrepresented in the capitalization table after a priced round of financing.
How to determine the SAFE conversion price on a pre or post-money basis
When the company closes a priced round of financing, a SAFE converts into company shares for SAFE holders. The number of shares a SAFE investor is entitled to is determined based on the conversion price (the valuation cap divided by the company capitalization, i.e., the total number of shares and options). You can do this on a pre or post-money basis.
What is the difference between a pre-money and a post-money calculation?
- Pre-money SAFE: the company capitalization excludes the shares that would be issued to the holders when the SAFE converts. This makes it more difficult to determine your ownership dilution as each conversion price is calculated independently.
- Post-money SAFE: the company capitalization includes all shares issued to holders when the SAFE converts. You will better understand your ownership dilution as all SAFEs will have converted into company shares.
The conversion price should be the same whether you calculate it on a pre or post-money basis. It is also important to note that pre and post-money only refer to the exclusion or inclusion of the shares subject to the company’s SAFEs, not the shares subject to the equity financing trigger.
Example: Post-money vs. pre-money valuation caps
ABC Inc.’s only outstanding securities are common shares comprising $6,000,000.
ABC Inc. wants to raise $4,000,000 through a SAFE round.
John gives ABC Inc. $2,000,000 on a SAFE with a Post-Money Valuation Cap.
Sara gives ABC Inc. $2,000,000 on a SAFE with a Pre-Money Valuation Cap.
John’s ownership:

John’s minimum ownership of ABC Inc. will be 20% before the equity financing.
Sara’s Ownership:

Sara’s minimum ownership of ABC Inc. will not be 33% before equity financing as the pre-money valuation cap does not consider John’s or Sara’s equity in ABC Inc. once their SAFEs convert. Sara will not know what her ownership % will be when she invests in ABC Inc.
SAFEs vs convertible notes
It is also common for startups to secure pre-seed or seed funding using convertible notes. A convertible note is a short-term debt that converts into equity. Investors loan money to the company, and instead of being repaid with interest, they receive preferred shares. Like SAFEs, convertible notes may have a valuation cap and discount rate.
A key difference between a convertible note and a SAFE is that a SAFE does not have an interest rate or a maturity date (the date the loan must be repaid if there has not been a conversion into equity). The interest that accrues on a convertible note must be repaid if the shares do not convert by the maturity date, or the interest rate can increase the number of shares the noteholder receives when the note converts.
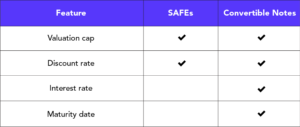
SAFEs are not debt. Under a SAFE, the company is not obligated to repay the investment unless a liquidity event or dissolution occurs. There is no guarantee that the SAFE will convert into company shares. Therefore, with SAFEs, the pressure to repay the investment as a maturity date approaches is not a concern, as it may be with a convertible note. SAFEs provide an alternative to convertible notes when a company is averse to debt.
Interested in discovering more on SAFEs, Convertible Notes or all things startup? Email MT>Ventures at info@mtventures.ca.
The content of this article is provided for general information purposes only and does not constitute legal or other professional advice or an opinion of any kind. Readers of this article are advised to seek specific legal advice by contacting members of MT>Ventures (or their own legal counsel) regarding any specific legal issues. Neither McCarthy Tetrault nor the DMZ warrants or guarantees the quality, accuracy or completeness of any information contained in this article. The information in this article is current as of its original date of publication but should not be relied upon as accurate, timely or fit for any particular.